Sum sales in last 30 days by ID in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Sum sales in last 30 days by ID in Excel using the example below:
Formula
=SUMIFS(amounts,dates,">="&TODAY()-30,ids,id)
Explanation
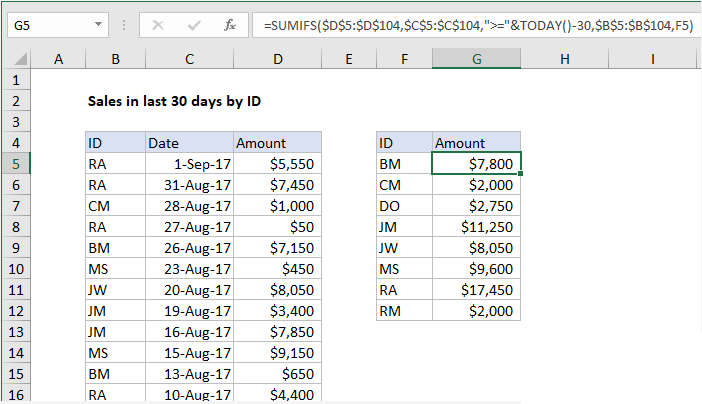
To sum sales in the last 30 days by an id (like name, initials, region, etc.) you can use the SUMIFS function together with the TODAY function. In the example shown, the formula in G5, copied down, is:
=SUMIFS($D$5:$D$104,$C$5:$C$104,">="&TODAY()-30,$B$5:$B$104,F5)
How this formula works
The SUMIFS function can handle multiple criteria when calculating a sum. In this case, SUMIFS is configured with a sum range for all amounts:
=SUMIFS($D$5:$D$104
The first criteria specifies a criteria range that contains all dates, with a criteria of greater than or equal to the current date minus 30:
=SUMIFS($D$5:$D$104,$C$5:$C$104,">="&TODAY()-30
The second criteria specifies a criteria range of all IDs, with a criteria of a single ID pulled from column F:
=SUMIFS($D$5:$D$104,$C$5:$C$104,">="&TODAY()-30,$B$5:$B$104,F5)
Note ranges for amounts, dates, and ids are absolute references, so that they won’t change when copied. When the formula is copied down column G, SUMIFS calculates total sales in the last 30 days for each ID in the table.
Total sales in the last 30 days
To get a sum for total sales in the last 30 days, just omit the second criteria:
SUMIFS(amounts,dates,">="&TODAY()-30)
For the example above, this becomes:
SUMIFS($D$5:$D$104,$C$5:$C$104,">="&TODAY()-30)