Position of first partial match in Excel
Formula
=MATCH("*text*",range,0)
Explanation
To get the position of the first partial match (i.e. the cell that contains text you are looking for) you can use the MATCH function with wildcards.
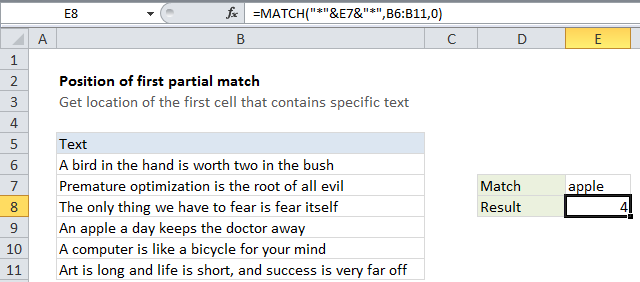
In the example shown, the formula in E8 is:
=MATCH("*"&E7&"*",B6:B11,0)
How this formula works
The MATCH function returns the position or “index” of the first match based on a lookup value in a range.
MATCH supports wildcard matching with an asterisk “*” (one or more characters) or a question mark “?” (one character), but only when the third argument, match_type, is set to FALSE or zero.
In the example, we pick up the value in cell E7 and use concatenation to combine this value with asterisks (*) on either side. The lookup array is the range B6 to B11, and match_type is set to zero to all partial matching with wildcards.
The result is the position of the first cell in the lookup range that contains the text “apple”.
To retrieve the value of a cell at a certain position, use the INDEX function.