How to use Excel CHOOSE Function
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the CHOOSE function with syntax and examples.
Excel CHOOSE function Description
The Microsoft Excel CHOOSE function returns a value from a list of values based on a given position.
The CHOOSE function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Lookup/Reference Function. It can be used as a worksheet function (WS) and a VBA function (VBA) in Excel. As a worksheet function, the CHOOSE function can be entered as part of a formula in a cell of a worksheet. As a VBA function, you can use this function in macro code that is entered through the Microsoft Visual Basic Editor.
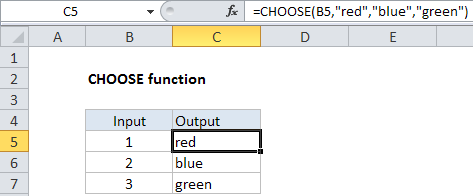
Explanation: The Excel CHOOSE function returns a value from a list using a given position or index. For example, CHOOSE(2,”red”,”blue”,”green”) returns “blue”, since blue is the 2nd value listed after the index number. The values provided to CHOOSE can include references.
Syntax
The syntax for the CHOOSE function in Microsoft Excel is:
CHOOSE( position, value1, [value2, ... value_n] )
Returns
The CHOOSE function returns any datatype such as a string, numeric, date, etc.
If position is less than 1, the CHOOSE function will return #VALUE!.
If position is greater than the number of the number of values in the list, the CHOOSE function will return #VALUE!.
Note: If position is a fraction (not an integer value), it will be converted to an integer by dropping the fractional component of the number.