How to create dynamic worksheet reference in Excel
To create a formula with a dynamic sheet name you can use the INDIRECT function.
Note: The point of this approach is it lets you to build a formula where the sheet name is a dynamic variable. So, for example, you could change a sheet name (perhaps with a drop down menu) and pull in information from different worksheet.
Formula
=INDIRECT(sheet_name&"!A1")
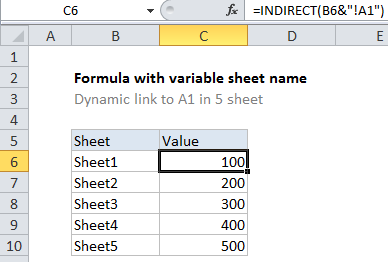
Explanation
In the example shown, the formula in C6 is:
=INDIRECT(B6&"!A1")
How this formula works
The INDIRECT function tries to evaluate text as a worksheet reference.
In this example, we have Sheet names in column B, so we join the sheet name to the cell reference A1 using concatenation:
=INDIRECT(B6&"!A1")
After concatenation, we have:
=INDIRECT("Sheet1!A1")
INDIRECT recognizes this as a valid reference to cell A1 in Sheet1, and returns the value in A1 (1000).
In cell C7, the formula evaluates like this:
=INDIRECT(B7&"!A1")
=INDIRECT("Sheet2!A1")
=200
And so on, for each formula in column C.
Handling spaces and punctuation in sheet names
If sheet names contain spaces, or punctuation characters, you’ll need to adjust the formula to wrap the sheet name in single quotes like this:
=INDIRECT("'"&sheet_name&"'!A1")
where sheet_name is a cell address like B6 in the example shown.