Count numbers by range with COUNTIFS in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Count numbers by range with COUNTIFS in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=COUNTIFS(range,">=low",range,"<=high")
Explanation
To count numeric data by range or grouping, you can build a summary table and use COUNTIFS to count values at each threshold.
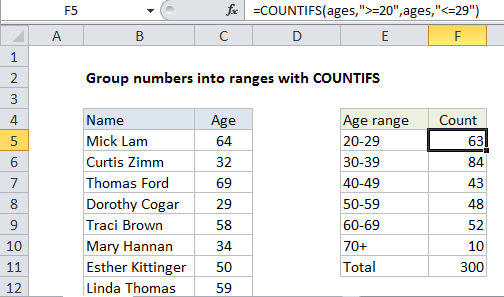
In the example show, we have a list of names and ages and are using the COUNTIFs function to generate a count of ages into 6 brackets. The formula in cell F5 is:
=COUNTIFS(ages,">=20",ages,"<=29")
How this formula works
The named range “ages” refers to C5:C304.
The COUNTIFS function lets you count values that meet multiple criteria with an AND relationship (i.e. all criterial must be true).
In this case, we want to group the data by age range into 10-year brackets, so we use COUNTIFS as follows in column F:
=COUNTIFS(ages,">=20",ages,"<=29") // 20-29 =COUNTIFS(ages,">=30",ages,"<=39") // 30-39 =COUNTIFS(ages,">=40",ages,"<=49") // 40-49
For the final bracket, 70+, we only use one criteria:
=COUNTIFS(ages,">=70") // 70+
Dynamic ranges
To expose ranges values on the worksheet where they can be easily changes, you can join references to logical operators with concatenation like this:
=COUNTIFS(ages,">="$A1,ages,"<="&B1)
This formula counts greater than or equal to (>=) the value in A1 and less than or equal to (>=)the value in B1.
With a Pivot Table
Pivot Tables offer automatic grouping into equal size ranges.