Group numbers with VLOOKUP in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Group numbers with VLOOKUP in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=VLOOKUP(value,group_table,column,TRUE)
Explanation
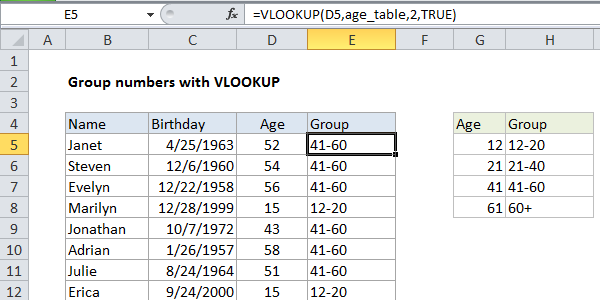
If you need to group by number, you can use the VLOOKUP function with a custom grouping table. This allows you to make completely custom or arbitrary groups.
In the example shown, the formula in F7 is:
=VLOOKUP(D5,age_table,2,TRUE)
How this formula works
This formula uses the value in cell D5 for a lookup value, the named range “age_table” (G5:H8) for the lookup table, 2 to indicate “2nd column”, and TRUE as the last argument indicate approximate match.
Note: the last argument is optional, and defaults to TRUE, but I like to explicitly set the matching mode.
VLOOKUP simply looks up the age and returns the group name from the 2nd column in the table. This column can contain any values that you wish.
Pivot tables
Pivot tables can automatically group numbers, but the VLOOKUP approach allows you to perform completely custom grouping.