How to remove trailing slash from url in Excel
To remove a trailing slash from a URL or path, you can use a formula based on the LEFT and LEN functions.
Formula
=LEFT(url,LEN(B4)-(RIGHT(url)="/"))
Explanation
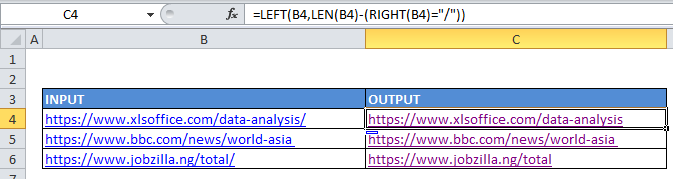
In the example shown, the formula in cell C6 is:
=LEFT(B4,LEN(B4)-(RIGHT(B4)="/"))
How this formula works
At the core, this formula uses the LEFT function to return text starting from the left. To work out how many characters should be returned, the formula uses this expression:
LEN(B4)-(RIGHT(B4)="/")
Here, total characters are calculated with the LEN function. From this number, the result of the following expression is subtracted:
RIGHT(B4)="/"
With number of characters not specified, RIGHT will return the last character in the string. If this characters is a forward slash “/”, the expression returns TRUE. If not, it returns FALSE.
Because TRUE and FALSE are coerced automatically to 1 and zero in math operations, we subtract zero from the result of LEN when the last characters is not “/” and we subtract 1 when the last characters is “/”.
The result is provided to LEFT, which returns the final result.