How to extract name from email address in Excel
If want to extract the name part of an email address, you can do so with a formula that uses the LEFT and FIND functions. In the formula below, email represents the email address you are working with.
Formula
=LEFT(email,FIND("@",email)-1)
Explanation
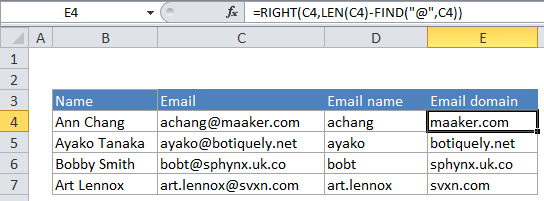
In the example, we are using this formula:
=LEFT(C4,FIND("@",C4)-1)
Here’s how the formula works:
At the core, this formula is extracting characters starting from the left, and using the FIND function to figure out how many characters to extract.
First, FIND looks for the “@” character inside the email address “achang@maaker.com”. The “@” character is the 7th character so FIND returns 7. The number 1 is then subtracted from 7 to yield 6. This is done to prevent the formula from extracting the “@” along with the name. The LEFT function then extracts 6 characters from the email address, starting from the left. So:
=LEFT(C4,FIND("@",C4)-1)
=LEFT("achang@maaker.com",FIND("@","achang@maaker.com")-1)
=LEFT("achang@maaker.com",7-1)
=LEFT("achang@maaker.com",6)
="achang"