How to extract domain from email address in Excel
Atimes a user may want to extract the domain from an email address, the RIGHT, LEN, and FIND functions can be used to achieve that. In the formula below, email represents the email address you are working with.
Formula
=RIGHT(email,LEN(email)-FIND("@",email))
Explanation
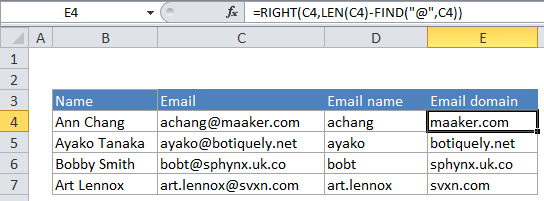
In the example, we are using this formula:
=RIGHT(C4,LEN(C4)-FIND("@",C4))
Here’s how the formula works
C4 contains the email address “achang@maaker.com”.
At the core, this formula is extracting characters starting from the right, and using the FIND and LEN functions to figure out how many characters to extract.
LEN computes the length of the entire email address, which 17 characters.
FIND locates the “@” character inside the email address “achang@maaker.com”. The “@” character is the 7th character, so FIND returns 7. The number 7 is then subtracted from the 17, which is 10. The number 10 is used as the second argument for the RIGHT function, which extracts 10 characters from the email address, starting from the right. The result is the domain, “maaker.com”
Altogether, this formula works something like this
=RIGHT(C4,LEN(C4)-FIND("@",C4))
=RIGHT(C4,17-7)
=RIGHT("achang@maaker.com",10)
="maaker.com"