How to create email address with name and domain in Excel
Atimes a user may want to build an email address from a first and last name. In that case, use a formula based on simple concatenation with help from the LEFT and LOWER functions. See illustration below:
Formula
=LOWER(LEFT(first)&last&"@"&domain)
Explanation
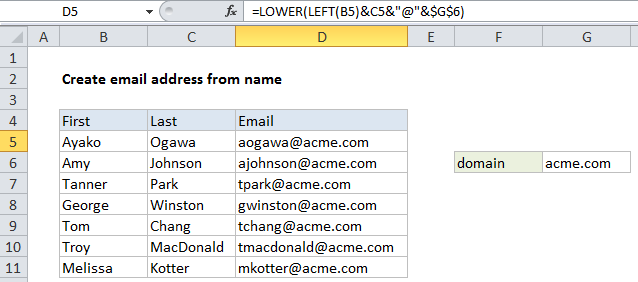
In the example shown, the formula in D5 is:
=LOWER(LEFT(B5)&C5&"@"&$G$6)
How this formula works
Working from the inside out, this formula first concatenates the last name in column C with the first letter of the first name from column B:
LEFT(B5)&C5
The LEFT function is normally configured with num_chars, but the argument is optional and left will extract 1 character from the left when it is absent. This results in the text string “atanaka”.
Next, the domain name is added like this:
"atanaka"&"@"&$G$6
Note that the reference to the domain name is absolute ($G$6) so that the formula can be copied down the table without this reference changing.
Finally, the lower function is used to lowercase the entire string:
=LOWER("ATanaka@acme.com")
which returns a final result of “atanaka@acme.com”