How to count total words in a cell in Excel
To count the total words in a cell, you can use a formula based on the LEN and SUBSTITUTE functions.
Formula
=LEN(A1)-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(A1," ",""))+1
Explanation
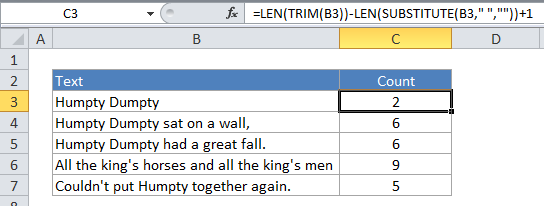
In the example shown, C3 contains this formula:
=LEN(TRIM(B3))-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B3," ",""))+1
How the formula works
SUBSTITUTE removes all spaces from the text, then LEN calculates the length of the text without spaces. This number is then subtracted from the length of the text with spaces, and the number 1 is added to the final result, since the number of words is the number of spaces + 1.
Dealing with empty cells
The formula in the example shown will return 1 even if a cell is empty. If you need to guard against this problem, using IF and ISBLANK:
=IF(ISBLANK(B3),0,LEN(TRIM(B3))-LEN(SUBSTITUTE(B3," ",""))+1)
Dealing with extra spaces
What about TRIM, what’s it doing in the formula? TRIM removes an extra spaces between words, or at the beginning or end of the text. So, before the length of the text with spaces is calculated, we use TRIM to make sure the text doesn’t contain any extra spaces, since extra spaces will throw the word count off.