VAR.P function: Description, Usage, Syntax, Examples and Explanation
What is VAR.P function in Excel?
VAR.P function is one of Statistical functions in Microsoft Excel that calculates variance based on the entire population (ignores logical values and text in the population).
Syntax of VAR.P function
VAR.P(number1,[number2],…)
The VAR.P function syntax has the following arguments:
- Number1: The first number argument corresponding to a population.
- Number2, … (Optional): Number arguments 2 to 254 corresponding to a population.
Explanation of VAR.P function
- VAR.P assumes that its arguments are the entire population. If your data represents a sample of the population, then compute the variance by using VAR.S.
- Arguments can either be numbers or names, arrays, or references that contain numbers.
- Logical values, and text representations of numbers that you type directly into the list of arguments are counted.
- If an argument is an array or reference, only numbers in that array or reference are counted. Empty cells, logical values, text, or error values in the array or reference are ignored.
- Arguments that are error values or text that cannot be translated into numbers cause errors.
- If you want to include logical values and text representations of numbers in a reference as part of the calculation, use the VARPA function.
- The equation for VAR.P is:
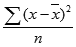 where x is the sample mean AVERAGE(number1,number2,…) and n is the sample size.
where x is the sample mean AVERAGE(number1,number2,…) and n is the sample size.
Example of VAR.P function
Steps to follow:
1. Open a new Excel worksheet.
2. Copy data in the following table below and paste it in cell A1
Note: For formulas to show results, select them, press F2 key on your keyboard and then press Enter.
You can adjust the column widths to see all the data, if need be.
| Strength | ||
| 1,345 | ||
| 1,301 | ||
| 1,368 | ||
| 1,322 | ||
| 1,310 | ||
| 1,370 | ||
| 1,318 | ||
| 1,350 | ||
| 1,303 | ||
| 1,299 | ||
| Formula | Description | Result |
| =VAR.P(A2:A11) | Variance of breaking strengths for all the tools, assuming that only 10 tools are produced (the entire population is used). | 678.84 |
| =VAR.S(A2:A11) | The variance, using the VAR.S function, which assumes only a sample of the population is tested. The result is different from VAR.P. | 754.27 |