TREND function: Description, Usage, Syntax, Examples and Explanation
What is TREND function in Excel?
Explanation of TREND function
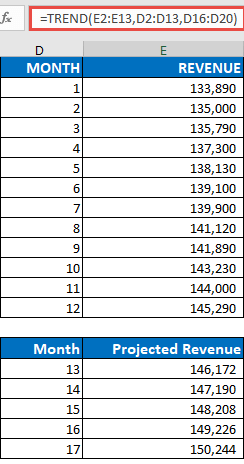
Note: If you have a current version of Office 365, then you can input the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range (cell E16 in this example), then press ENTER to confirm the formula as a dynamic array formula. Otherwise, the formula must be entered as a legacy array formula by first selecting the output range (E16:E20), input the formula in the top-left-cell of the output range (E16), then press CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER to confirm it. Excel inserts curly brackets at the beginning and end of the formula for you.