POISSON.DIST function: Description, Usage, Syntax, Examples and Explanation
What is POISSON.DIST function in Excel?
POISSON.DIST function is one of Statistical functions in Microsoft Excel that returns the Poisson distribution. A common application of the Poisson distribution is predicting the number of events over a specific time, such as the number of cars arriving at a toll plaza in 1 minute.
Syntax of POISSON.DIST function
POISSON.DIST(x,mean,cumulative)
The POISSON.DIST function syntax has the following arguments:
- X: The number of events.
- Mean: The expected numeric value.
- Cumulative: A logical value that determines the form of the probability distribution returned. If cumulative is TRUE, POISSON.DIST returns the cumulative Poisson probability that the number of random events occurring will be between zero and x inclusive; if FALSE, it returns the Poisson probability mass function that the number of events occurring will be exactly x.
Explanation of POISSON.DIST function
- If x is not an integer, it is truncated.
- If x or mean is nonnumeric, POISSON.DIST returns the #VALUE! error value.
- If x < 0, POISSON.DIST returns the #NUM! error value.
- If mean < 0, POISSON.DIST returns the #NUM! error value.
- POISSON.DIST is calculated as follows.For cumulative = FALSE:
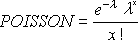
For cumulative = TRUE:
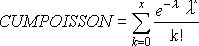
Example of POISSON.DIST function
Steps to follow:
1. Open a new Excel worksheet.
2. Copy data in the following table below and paste it in cell A1
Note: For formulas to show results, select them, press F2 key on your keyboard and then press Enter.
You can adjust the column widths to see all the data, if need be.
| Data | Description | |
| 2 | Number of events | |
| 5 | Expected mean | |
| Formula | Description | Result |
| =POISSON.DIST(A2,A3,TRUE) | Cumulative Poisson probability with the arguments specified in A2 and A3. | 0.124652 |
| =POISSON.DIST(A2,A3,FALSE) | Poisson probability mass function with the arguments specified in A2 and A3. | 0.084224 |