How to get last row in mixed data with no blanks in Excel
To get the last relative position (i.e. last row, last column) for mixed data that contains no empty cells, you can use the COUNTA function. See example below:
Formula
=COUNTA(range)
Explanation
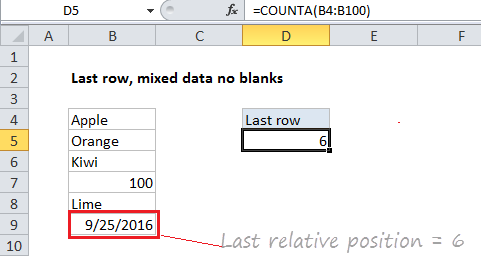
In the example shown, the formula in D5 is:
=COUNTA(B4:B100)
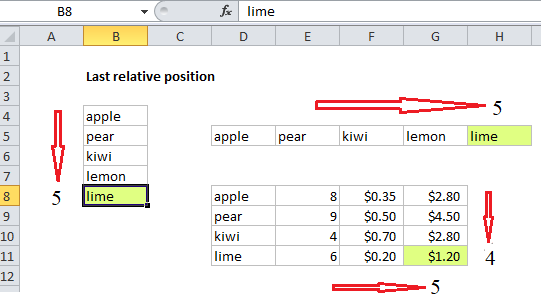
Last *relative* position
When constructing more advanced formulas, it’s often necessary to figure out the last location of data in a list. Depending on the data, this could be the last row with data, the last column with data, or the intersection of both. It’s important to understand that we are after the last *relative position* inside a given range not the row number on the worksheet:
How this formula works
This formula uses the COUNTA function to count values in a range. COUNTA counts both numbers and text to so works well with mixed data.
The range B4:B8 contains 5 values, so COUNTA returns 5. The number 5 corresponds to the last row (last relative position) of data in the range B4:B100.
Note: This approach will fail if the range contains blank/empty cells.