Round numbers in Excel
This chapter illustrates three Mathematical functions ROUND, ROUNDUP and ROUNDDOWN.
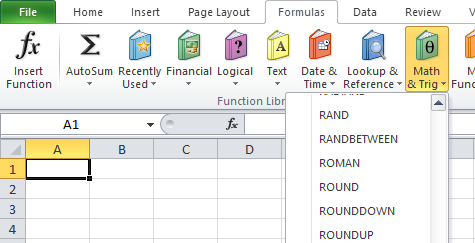
Navigation: Formula Tab → Function Library Group → Math & Trig Category
Before your start: if you round a number, you lose precision. If you don’t want this, show fewer decimal places without changing the number itself.
Round
Syntax:
ROUND(number, num_digits)
1. Round a number to two decimal places.
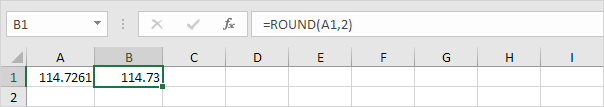
Note: 1, 2, 3, and 4 get rounded down. 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 get rounded up. In this example, 114.7211, 114.7221, 114.7231 and 114.7241 get rounded down to 114.72 and 114.7251, 114.7261, 114.7271, 114.7281 and 114.7291 get rounded up to 114.73.
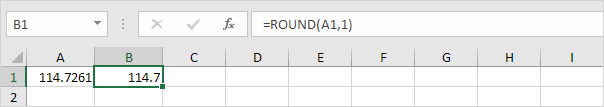
2. Round a number to one decimal place.
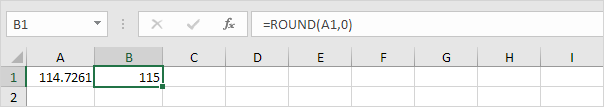
3. Round a number to the nearest integer.
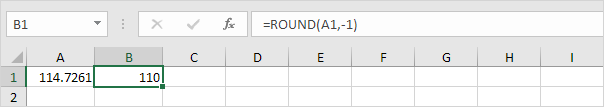
4. Round a number to the nearest 10.
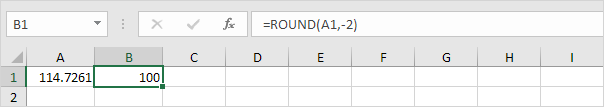
5. Round a number to the nearest 100.
RoundUp
Syntax:
ROUNDUP(number, num_digits)
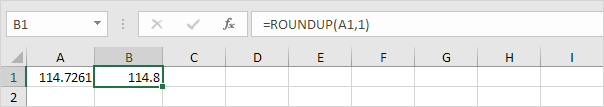
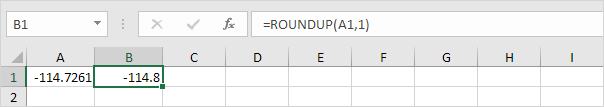
The ROUNDUP function always rounds a number up (away from zero). For example, round a number up to one decimal place.
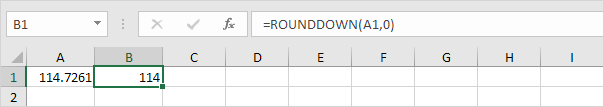
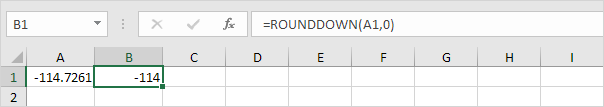
RoundDown
Syntax:
ROUNDDOWN(number, num_digits)
The ROUNDDOWN function always rounds a number down (toward zero). For example, round a number down to the nearest integer.