How to check cell equals one of many things in Excel
If you want to test a cell to see if it equals one of several things, you can do so with a formula that uses the SUMPRODUCT function.
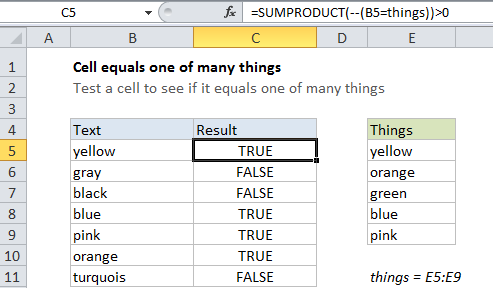
Case study: Let’s say you have a list of text strings in the range B5:B11, and you want to test each cell against another list of things in range E5:E9. In other words, for each cell in B5:B11, you want to know: does this cell equal any of the things in E5:E9?
You could start build a big formula based on nested IF statements, but an array formula based on SUMPRODUCT is a simpler, cleaner approach.
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT(--(A1=things))>0
Explanation
The solution is to to create a formula that will test for multiple values and return a list of TRUE / FALSE values. Once we have that, we can process that list (an array, actually) with SUMPRODUCT.
The formula we’re using looks like this:
=SUMPRODUCT(--(B5=things))>0
How this formula works
The key is this snippet:
--(B5=things)
which simply compares the value in B5 to every value in the named range “things”. Because we are comparing B5 to an array (i.e. the named range “things”, E5:E11) the result will be an array of TRUE / FALSE values like this:
{TRUE;FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;FALSE}
If we have even one TRUE in the array, we know that B5 equals at least one thing in the list, so, to force the TRUE / FALSE values to 1s and 0s, we use a double negative (–, also called a double unary). After this coercion, we have this:
{1;0;0;0;0}
Now we process the result with SUMPRODUCT, which will add up the elements in the array. If we get any non-zero result, we have at least one match, so we use >1 to force a final result of either TRUE or FALSE.
With a hard-coded list
There’s no requirement that you use a range for your list of things. If you’re only looking for a small number of things, you can use a list in array format, which is called an array constant. For example, if you’re just looking for the colors red, blue, and green, you can use {“red”,”blue”,”green”} like this:
--(B5={"red","blue","green"})
Dealing with extra spaces
If the cells you are testing contain any extra space, they won’t match properly. To strip all extra space, you can modify the formula to use the TRIM function like so:
=SUMPRODUCT(--(TRIM(A1)=things))>0