How to use Excel XOR Function
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the XOR function with syntax and examples.
Excel XOR Function Function Description
Excel XOR function performs what is called “exclusive OR”.
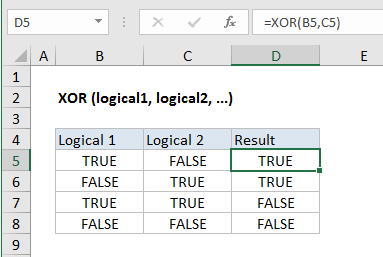
The XOR function returns the Exclusive Or logical operation for one or more supplied conditions. With two logical statements, XOR returns TRUE if either statement is TRUE, but returns FALSE if both statements are TRUE. If neither is TRUE, XOR also returns FALSE.
XOR Function Examples
Explanation:
Base on the example above, the XOR function returns TRUE if an odd number of the supplied conditions evaluate to TRUE, and FALSE otherwise.
Syntax
The syntax of the function is:
Arguments
where the logical_test arguments are between 1 and 254 supplied conditions that evaluate to either TRUE or FALSE.
Note that:
- If the logical_test arguments evaluate to numbers, instead of logical values, the value zero is treated as FALSE and all non-zero values are treated as TRUE
- XOR was introduced in Excel 2013.
Return
TRUE or FALSE
With more than 2 logicals
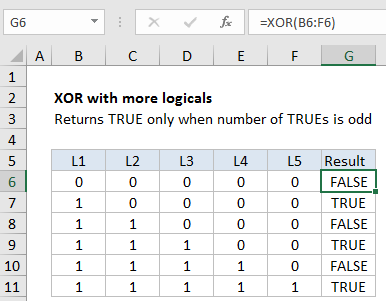
With more than 2 logicals, XOR only returns TRUE when the number of TRUE logicals is odd, as shown in the following example:
Notes:
- Logical arguments must evaluate to TRUE or FALSE, 1 or 0, or be references that contain logical values.
- Empty references are ignored.
- XOR returns #VALUE! if no logical values are found.
- With more than two logicals, XOR returns TRUE when the number of TRUE logicals is odd, and FALSE if not.