How to set check register balance in Excel
This tutorial shows how to set a check register formula that calculates a running balance and also, blank values using formula based on simple addition and subtraction.
See illustrations below:
Formula
=balance-debit+credit
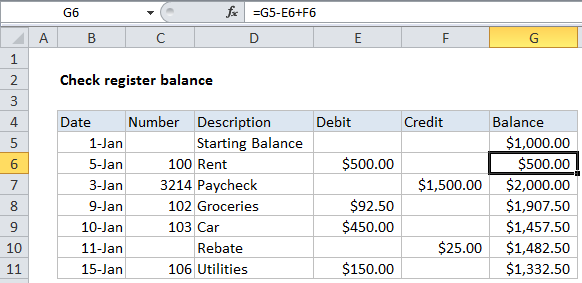
Explanation
In the example shown, the formula in G6 is:
=G5-E6+F6
How this formula works
The value in G5 is hard-coded. The formula picks up the value in G5, then subtracts the value (if any) in E6 and adds the value (if any) in F6. When the credit or debit values are empty, they behave like zero and have no effect on the result.
When this formula is copied down column G, it will continue to calculate a running balance in each row.
Dealing with blank values
To display nothing in the balance column when the credit and debit columns are empty, you can use the IF function with AND and ISBLANK like this:
=IF(AND(ISBLANK(E6),ISBLANK(F6)),"",G5-E6+F6)
Note: this only handles bank credit and debit values at the end of the table, not rows in between.
This formula will return an empty string (“”) when both credit and debit cells are empty, and return the running balance if either number exists.