PMT, RATE, NPER, PV and FV Financial Functions in Excel
Learn all about Excel’s PMT, RATE, NPER, PV and FV
To illustrate Excel’s most popular financial functions, we consider a loan with monthly payments, an annual interest rate of 6%, a 20-year duration, a present value of $150,000 (amount borrowed) and a future value of 0 (that’s what you hope to achieve when you pay off a loan).
We make monthly payments, so we use 6%/12 = 0.5% for Rate and 20*12 = 240 for Nper (total number of periods). If we make annual payments on the same loan, we use 6% for Rate and 20 for Nper.
PMT:
Calculates the payment for a loan based on constant payments and a constant interest rate.Syntax for PMT:
PMT(rate, nper, pv, [fv], [type])
Select cell A2 and insert the PMT function.
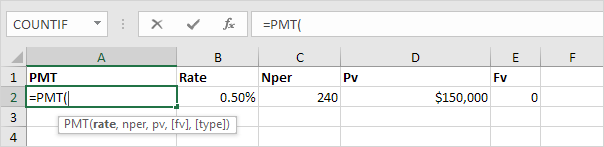
Note: the last two arguments are optional. For loans, Fv can be omitted (the future value of a loan equals 0, however, it’s included here for clarification). If Type is omitted, it is assumed that payments are due at the end of the period.
Result. The monthly payment equals $1,074.65.
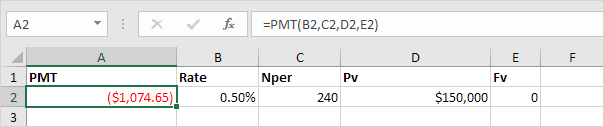
Tip: when working with financial functions in Excel, always ask yourself the question, am I making a payment (negative) or am I receiving money (positive)? We pay off a loan of $150,000 (positive, we received that amount) and we make monthly payments of $1,074.65 (negative, we pay). Visit our page about the PMT function for many more examples.
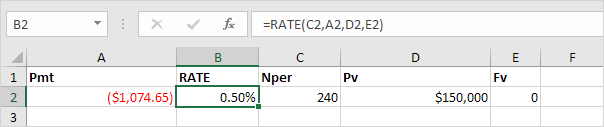
RATE:
Returns the interest rate per period of an annuity.Syntax for RATE:
RATE(nper, pmt, pv, [fv], [type], [guess])
If Rate is the only unknown variable, we can use the RATE function to calculate the interest rate.
NPER:
Returns the number of periods for an investment based on periodic, constant payments and a constant interest rate. Syntax for NPER:
NPER(rate,pmt,pv,[fv],[type])
Or the NPER function. If we make monthly payments of $1,074.65 on a 20-year loan, with an annual interest rate of 6%, it takes 240 months to pay off this loan.
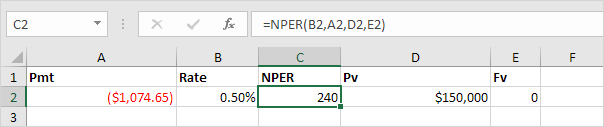
We already knew this, but we can change the monthly payment now to see how this affects the total number of periods.

Conclusion: if we make monthly payments of $2,074.65, it takes less than 90 months to pay off this loan.
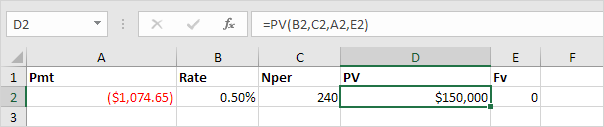
PV:
Returns the present value of an investment.
Syntax for PV:
PV(rate, nper, pmt, [fv], [type])
Or the PV (Present Value) function. If we make monthly payments of $1,074.65 on a 20-year loan, with an annual interest rate of 6%, how much can we borrow? You already know the answer.
FV:
Returns the future value of an investment based on periodic, constant payments and a constant interest rate.
Syntax for FV:
FV(rate,nper,pmt,[pv],[type])
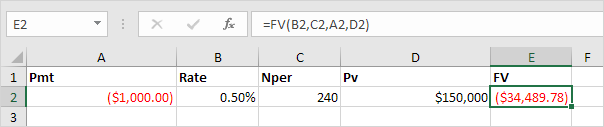
And we finish this chapter with the FV (Future Value) function. If we make monthly payments of $1,074.65 on a 20-year loan, with an annual interest rate of 6%, do we pay off this loan? Yes.
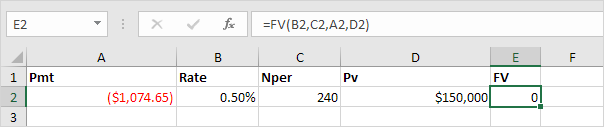
But, if we make monthly payments of only $1,000.00, we still have debt after 20 years.