Example of payment for annuity in Excel
This tutorial shows how to solve for an annuity payment in Excel. An annuity is a series of equal cash flows, spaced equally in time.
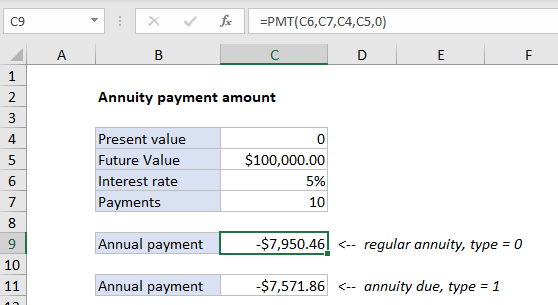
Case study: Using the PMT function, the goal in this example is to have 100,000 at the end of 10 years, with an interest rate of 5%. Payments are made annually, at the end of each year.
Formula
=PMT(rate,nper,pv,fv,type)
Explanation
In the example shown C9 contains this formula:
=PMT(C6,C7,C4,C5,0)
Explanation
To solve for the payment required, the PMT function is configured like this:
- nper – from cell C7, 25.
- pv – from cell C4, 0.
- rate – from cell C6, 5%.
- fv – from cell C5, 100000.
- type – 0, payment at end of period (regular annuity).
With this information, the PMT function returns -$7,950.46. The value is negative because it represents a cash outflow.
Annuity due
With an annuity due, payments are made at the beginning of the period, instead of the end. To calculate the payment for an annuity due, use 1 for the type argument. In the example shown, the formula in C11 is:
=PMT(C6,C7,C4,C5,1)
which returns -$7,571.86 as the payment amount. Notice the only difference in this formula is type = 1.