How to get workdays between dates in Excel
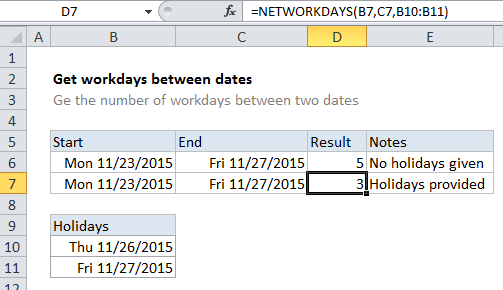
To calculate the number of workdays between two dates, you can use the NETWORKDAYS function. NETWORKDAYS automatically excludes weekends, and it can optionally exclude a custom list of holidays as well.
Formula
=NETWORKDAYS(start_date,end_date,holidays)
Explanation
For example, if you have the date January 4, 2016 (a Monday) in cell B4, and January 11, 2016 (also a Monday) in cell C4, this formula will return 6:
=NETWORKDAYS(B4,C4)
NETWORKDAYS can also exclude a custom list of holidays. For example, if you have holiday dates in H1:H10, you can tell NETWORKDAYS not to include these dates as workdays by adding that range as a third argument in the formula:
=NETWORKDAYS(B4,C4,H1:H10)
Custom weekends
If you need take into account custom weekends (i.e. weekends are Saturday only, Sunday and Monday, etc.) you’ll need to switch to the more robust NETWORKDAYS.INTL function, which allows you to set what days of the week are considered are considered weekends, by supplying a weekend argument in the form of a numeric code.