Get days before a date in Excel
To calculate the number of days before a certain date in Excel, you can use subtraction and the TODAY function. See example below:
Formula
=date-TODAY()
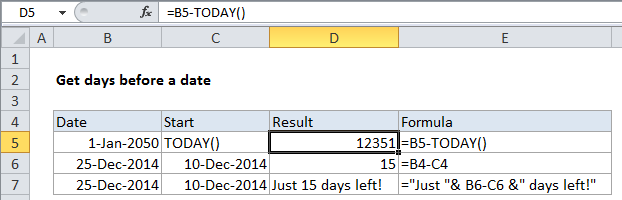
Explanation
In the example, D5 contains this formula:
=B4-TODAY()
How this formula works
In Excel, dates are simply serial numbers. In the standard date system for windows, based on the year 1900, where January 1, 1900 is the number 1. Dates are valid through 9999, which is serial number 2,958,465. This means that January 1, 2050 is the serial number 54,789.
In the example, the date is March 9, 2016, which is the serial number 42,438. So:
= B4-TODAY() = January 1 2050 - April 27, 2014 = 54,789 - 42,438 = 12,351
This means there are 13,033 days before January 1, 2050, when counting from March 9, 2016.
Without TODAY
Note: you don’t need to use the TODAY function. In the second example, the formula in D6 is:
=B6-C6
Concatenating with text
In the third example, the same basic formula is used along with concatenation operator (&) to embed the calculated days in a simple text message:
="Just "& B6-C6 &" days left!"
Since there are 15 days between December 10, 2014 and December 25, 2014, the result is this message: Just 15 days left!