DATE function: Description, Usage, Syntax, Examples and Explanation
What is DATE function in Excel?
Syntax of DATE function
The syntax for the DATE function in Microsoft Excel is:
DATE( year, month, day )
DATE formula explanation
- Year: A number that is between one and four digits that represents the year.
- Month: A number representing the month value. If the month value is greater than 12, then every 12 months will add 1 year to the year value. This means that DATE(2016,13,4) is equal to DATE(2017,1,4) and DATE(2016,25,4) is equal to DATE(2018,1,4) … and so on.
- Day: A number representing the day value. If the day value is greater than the number of days in the month specified, then the appropriate number of months will be added to the month value.
Returns
The DATE function returns a serial date value. A serial date is how Excel stores dates internally and it represents the number of days since January 1, 1900.
If the year is greater than 9999, the DATE function will return the #NUM! error.
Note
- If the year is between 0 and 1899, the year value is added to 1900 to determine the year.
- If the year is between 1900 and 9999, the DATE function uses the year value as the year.
Examples of DATE function
The example illustrated below shows DATE function result as an unformatted serial date in column D and column E show you the result as a formatted date in mm/d/yyyy.
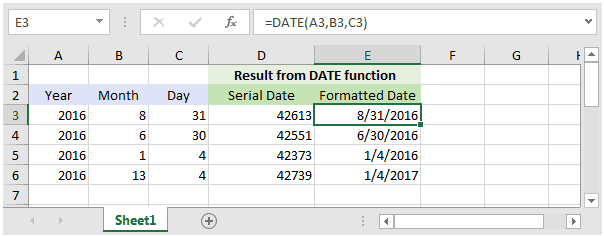
Based on the Excel spreadsheet above, the following DATE examples would return:
=DATE(A3,B3,C3) Result: 42613 'Which can be formatted as "8/31/2016" =DATE(A4,B4,C4) Result: 42551 'Which can be formatted as "6/30/2016" =DATE(A5,B5,C5) Result: 42373 'Which can be formatted as "1/4/2016" =DATE(A6,B6,C6) Result: 42739 'Which can be formatted as "1/4/2017"
Notice in the last example =DATE(B6,B6,C6) that the month value is 13 and larger than 12. In this example, 1 would be added to the year making it 2017. And the remainder of 1 would used as the month value.