Count holidays between two dates in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Count holidays between two dates in Excel using example below.
To count holidays that occur between two dates, you can use the SUMPRODUCT function.
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT((holidays>=start)*(holidays<=end))
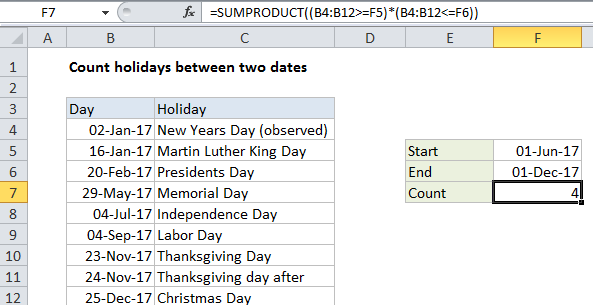
Explanation
In the example shown, the formula in F8 is:
=SUMPRODUCT((B4:B12>=F5)*(B4:B12<=F6))
How this formula works
This formula uses two expressions in a single array inside the SUMPRODUCT function.
The first expression tests every holiday date to see if it’s greater than or equal to the start date in F5:
(B4:B12>=F5)
This returns an array of TRUE/FALSE values like this:
{FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;FALSE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE}
The second expression tests every holiday date to see if it’s less than or equal to the end date in F6:
(B4:B12<=F6)
which returns an array of TRUE/FALSE values like this:
{TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;TRUE;FALSE}
The multiplication of these two arrays automatically coerces the TRUE/FALSE values to ones and zeros, resulting in arrays that look like this:
=SUMPRODUCT(({0;0;0;0;1;1;1;1;1})*({1;1;1;1;1;1;1;1;0}))
After multiplication, we have just one array like this:
=SUMPRODUCT({0;0;0;0;1;1;1;1;0})
Finally, SUMPRODUCT sums the items in the array and returns 4.
Holidays on weekdays only
To count holidays that occur on weekdays only (Mon-Fri), you can extend the formula like this:
=SUMPRODUCT((range>=F5)*(range<=F6)*(WEEKDAY(range,2)<6))