Convert decimal seconds to Excel time
This tutorial shows how to Convert decimal seconds to Excel time using example below.
To convert seconds in decimal format to a proper Excel time, divide by 86400.
Formula
=seconds/86400
Explanation
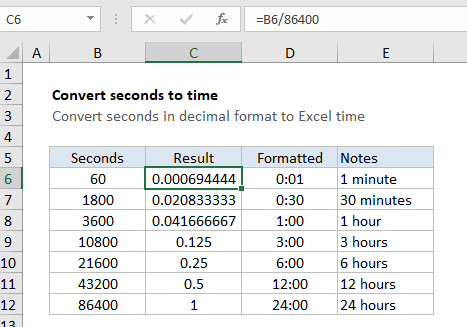
In the example shown, the formula in C6 is:
=B6/86400
To display the result as time, apply a time format. Column D shows the same result formatted with [h]:mm.
How this formula works
In the Excel date system, one day is equal to 1, so you can think of time as fractional values of 1, as shown in the table below:
| Hours | Fraction | Minutes | Seconds | Value | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1/24 | 60 | 3600 | 0.04167 | 1:00 |
| 3 | 3/24 | 180 | 10800 | 0.125 | 3:00 |
| 6 | 6/24 | 360 | 21600 | 0.25 | 6:00 |
| 12 | 12/24 | 720 | 43200 | 0.5 | 12:00 |
| 18 | 18/24 | 1080 | 64800 | 0.75 | 18:00 |
| 24 | 24/24 | 1440 | 86400 | 1.0 | 21:00 |
Since there are 24 hours in a day, 60 minutes in each hour, and 60 seconds in each minute, you need to divide by 24 * 60 * 60 = 86400 in order to convert decimal seconds to a value that Excel will recognize as time. After dividing by 86400, you can apply a time format of your choice, or use the result in a math operation with other dates or times.
In the example, since B11 contains 43200 (representing 43200 seconds, or a half day) the result is 43200/86400 = 0.5. Once a time format like h:mm or [h]:mm is applied, Excel will display 12:00.
Displaying a time duration
To display hours that represent a duration longer than 24 hours, minutes in durations longer than 60 minutes, or seconds in durations over 60 seconds, you’ll need to adjust the number format by adding square brackets.
[h] // for hours greater than 24 [m] // for minutes greater than 60 [s] // for seconds greater than 60
The brackets tell to Excel the time is a duration, and not a time of day.
Note: to use square brackets, you’ll need to create and apply a custom number format. Select cells, then go to Format Cells (Control + 1) > Number > Custom.