Calculate total hours that fall between two times in Excel
Case study
You have a start time and an end time, and you want to know how many of the hours in between these two times overlap another time period in the day. For example, you want to know how many hours fall between 8:00 AM and 5:00 PM, or 7:00 PM to 7:00 AM, etc.
You might need this information to calculate different hourly rates or different service charges depending on what time of day the work occurred. For instance, you might pay one rate for hours logged between 7:00 PM to 7:00 AM and a different rate for hours outside that period.
Formula
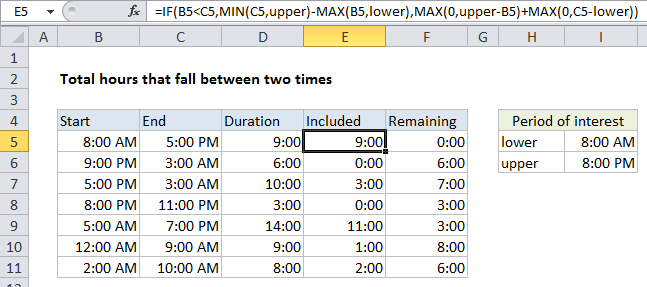
=IF(start<end,MIN(end,upper)-MAX(start,lower),MAX(0,upper-start)+MAX(0,end-lower))
Explanation
Approach
In this example, we first calculate the total hours between the start time and end time. Then we figure out the total hours that overlap “the period of interest”. Using these two values, we can figure out all remaining hours.
In all formulas, “lower” represents the first time (lower bound) in the time period of interest, and upper represents the second time (upper bound).
Formulas
To calculate total hours between start and end time, the formula in D5 is:
=MOD(C5-B5,1)
This formula is explained in more detail here.
The formula in E5 works in two parts, using IF to control flow. If the start time is less than the end time, we calculate the overlap with period of interest with:
MIN(C5,upper)-MAX(B5,lower)
If the start time is greater than end time (i.e. start time and end times cross a midnight), we use:
MAX(0,upper-B5)+MAX(0,C5-lower)
By using MAX with zero, we prevent negative values from being used.
Finally, to figure out “Remaining” hours (i.e. hours that do not fall in the period of interest) we simply subtract E5 (included) from D5 (total duration).