Basic timesheet formula with breaks in Excel
This tutorials shows Basic timesheet formula with breaks in Excel.
To calculate work hours, taking into account break time that needs to be subtracted, you can use a formula based on the MOD function. MOD is used to handle start and end times that cross midnight.
Formula
=MOD(workstart-workend,1)-MOD(breakstart-breakend,1)
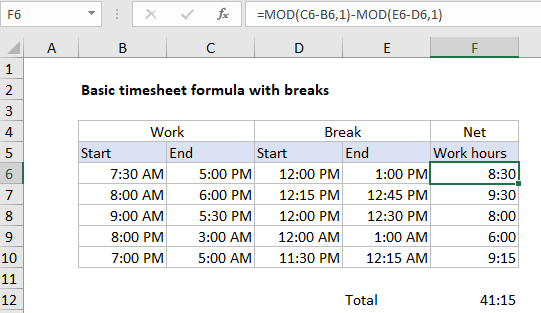
Explanation
In the example shown, the formula in F6 is:
=MOD(C6-B6,1)-MOD(E6-D6,1)
How this formula works
At the core, this formula subtracts start time from end time to get duration in hours. This is done to calculate both work time and break time.
MOD(C6-B6,1) // get work time MOD(E6-D6,1) // get break time
Next, break time is subtracted from work time to get “net work hours”.
This formula uses the the MOD function to handle times that cross a day boundary (midnight). By using MOD with a divisor of 1, positive results are unchanged, but negative results (which occur when start time is greater than end time) are “flipped” to get a correct duration.
For more details, see: How to calculate number of hours between two times
Alternative timesheet layout
The screenshot below shows an alternative format to capture time worked. Instead of logging work and break time separately, this version captures two separate in/out times for a single shift.
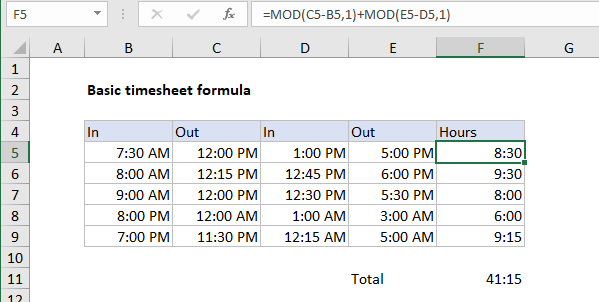
For this layout, the formula used in F5 is:
=MOD(C5-B5,1)+MOD(E5-D5,1)
Instead of subtracting break time from work time, we add together two work times.