Excel Data validation don’t exceed total
Using the example below, this tutorial shows how to create Data validation don’t exceed total in Excel.
Formula
=SUM(range)<=1000
 Explanation
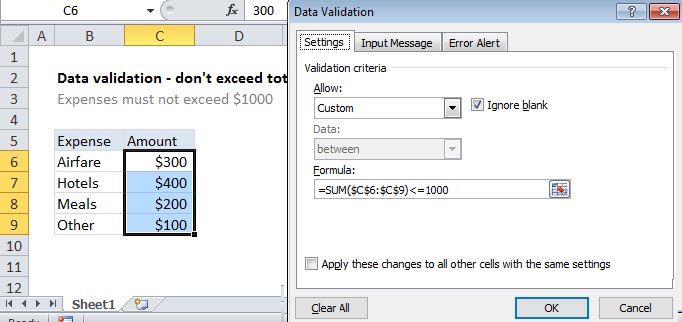
Explanation
To allow only values that don’t exceed a set sum, you can use data validation with a custom formula based on the SUM function. In the example shown, the data validation applied to B5:B9 is:
=SUM($C$6:$C$9)<=1000
How this formula works
Data validation rules are triggered when a user adds or changes a cell value.
In this case, we need a formula that returns FALSE as long as entries in C6:C9 sum to a total equal to or below 1000. We use the SUM function to sum a fixed range and then simply compare the result to 1000 using less than or equal to. Note the range C6:C9 is entered as an absolute reference to prevent the reference from changing automatically for each cell that data validation is applied to.
Each time a number is entered, the validation is triggered. As long as the sum remains less than 1000, validation succeeds. If any entry causes the sum C6:C9 to exceed 1000, validation fails.
Note: Cell references in data validation formulas are relative to the upper left cell in the range selected when the validation rule is defined, in this case B5.