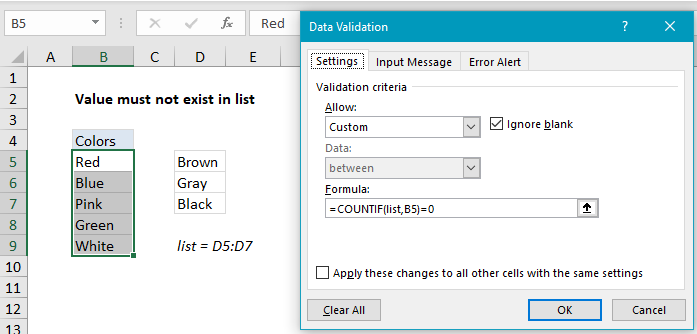
Data validation must not exist in list
Accept data that are not included in a specific range of records
To allow only values that do not exist in a list, you can use data validation with a custom formula based on the COUNTIF function.
Note: Excel has a built-in data validation rules for dropdown lists. This page explains how to create a custom validation rule when you want to *prevent* a user from entering a value in a list.
Formula
=COUNTIF(list,A1)=0
 Explanation
Explanation
Based on the example above, the data validation applied to B5:B9 is:
=COUNTIF(list,B5)=0
where “list” is the named range D5:D7.
How this formula works
Data validation rules are triggered when a user adds or changes a cell value.
In this case, the COUNTIF function is part of an expression that returns TRUE when a value does not exist in a defined list. The COUNTIF function simply counts occurrences of the value in the list. As long as the count is zero, the entry will pass validation. If the count is not zero (i.e. the user entered a value from the list) validation will fail.