Working With Tables in Excel
Tables allow you to analyze your data in Excel quickly and easily.
Learn how to insert, sort and filter a table, and how to display a total row at the end of a table.
Navigation: Insert Tab → Tables Group – Table
Insert a Table
To insert a table, execute the following steps.
1. Click any single cell inside the data set.
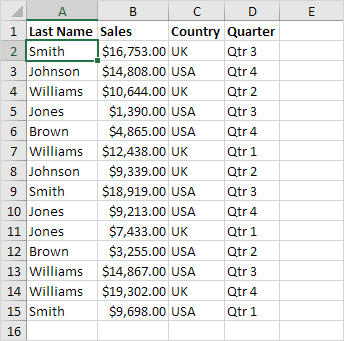
2. On the Insert tab, in the Tables group, click Table.

3. Excel automatically selects the data for you. Check ‘My table has headers’ and click on OK.
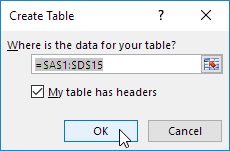
Result. Excel creates a nicely formatted table for you. This may still seem like a normal data range to you but many powerful features are now just a click of a button away.
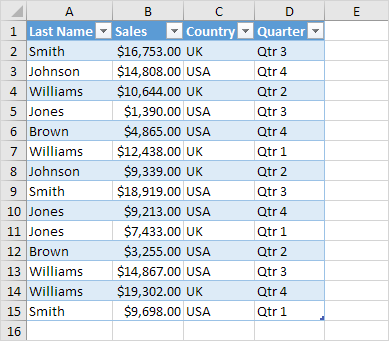
Sort a Table
To sort by Last Name first and Sales second, execute the following steps.
1. Click the arrow next to Sales and click Sort Smallest to Largest.
2. Click the arrow next to Last Name and click Sort A to Z.
Result.
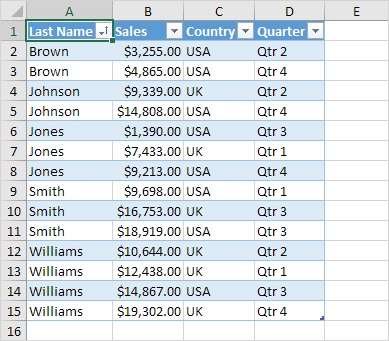
Filter a Table
To filter a table, execute the following steps.
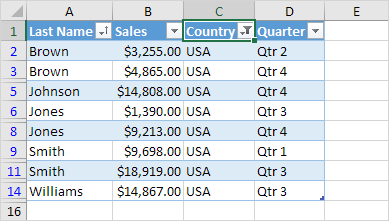
1. Click the arrow next to Country and only check USA.
Result.
Total Row
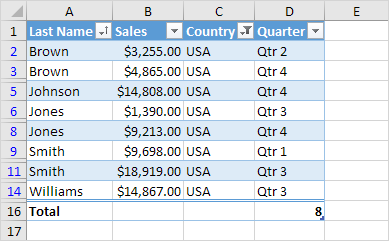
To display a total row at the end of the table, execute the following steps.
1. First, select a cell inside the table. Next, on the Design tab, in the Table Style Options group, check Total Row.

Result.
2. Click any cell in the last row to calculate the Total (Average, Count, Max, Min, Sum etc.) of a column. For example, calculate the sum of the Sales column.
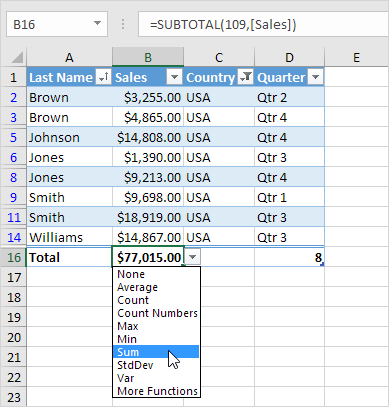
Note: in the formula bar see how Excel uses the SUBTOTAL function to calculate the sum. 109 is the argument for Sum if you use the SUBTOTAL function. Excel uses this function (and not the standard SUM function) to correctly calculate table totals of filtered tables.
Also, Excel tables should not be confused with the data tables (data table: A range of cells that shows the results of substituting different values in one or more formulas. There are two types of data tables: one-input tables and two-input tables.) that are part of a suite of what-if analysis commands.
