Understanding Named Range, Named Constant, Name Manager in Excel Formulas
By using names you can make your formulas much easier to understand and maintain i.e to update, audit, and manage.
You can define a name for a cell range, function, constant, or table.
Name: A word or string of characters in Excel that represents a cell, range of cells, formula, or constant value.
Named Range
To create a named range, execute the following steps.
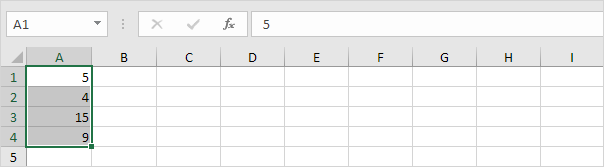
1. Select the range A1:A4.
2. On the Formulas tab, in the Defined Names group, click Define Name.
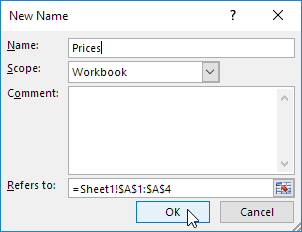
3. Enter a name and click OK.
There’s an even quicker way of doing this.
4. Select the range, type the name in the Name box and press Enter.

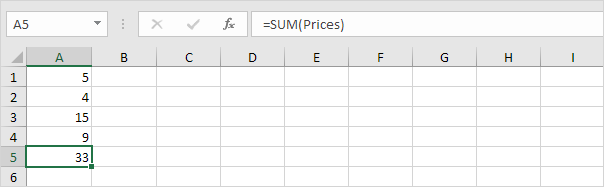
5. Now you can use this named range in your formulas. For example, sum Prices.
Named Constant
To create a named constant, execute the following steps.
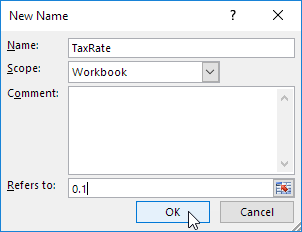
1. On the Formulas tab, in the Defined Names group, click Define Name.

2. Enter a name, type a value, and click OK.
3. Now you can use this named constant in your formulas.
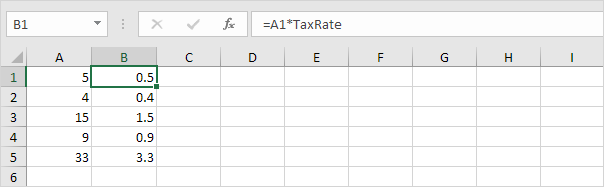
Note: if the tax rate changes, use the Name Manager to edit the name and Excel automatically updates all the formulas that use TaxRate.
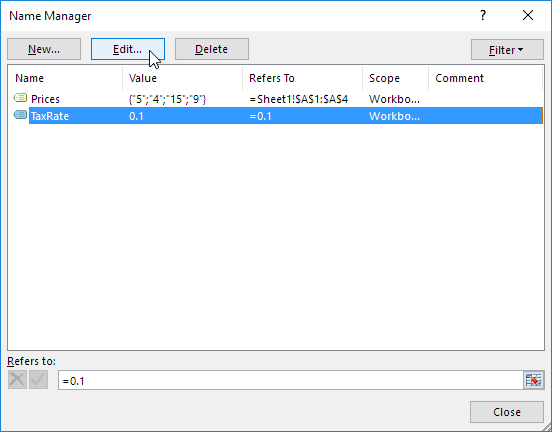
Name Manager
To edit and delete defined names, execute the following steps.
1. On the Formulas tab, in the Defined Names group, click Name Manager.
2. For example, select TaxRate and click Edit.