Calculate Compound Interest in Excel
What’s compound interest and what’s the formula for compound interest in Excel?
How to Calculate Compound Interest in Excel
This example gives you the answers to these questions.
1. Assume you put $100 into a bank. How much will your investment be worth after one year at an annual interest rate of 8%?
The answer is $108.
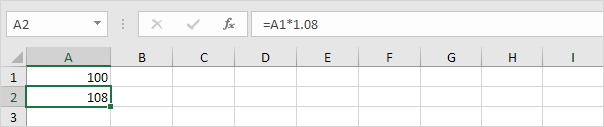
2. Now this interest ($8) will also earn interest (compound interest) next year. How much will your investment be worth after two years at an annual interest rate of 8%? The answer is $116.64.
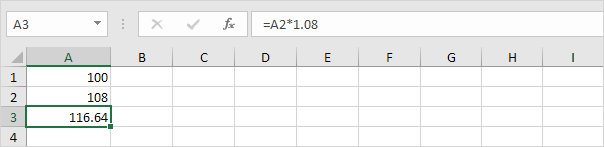
3. How much will your investment be worth after 5 years? Simply drag the formula down to cell A6.
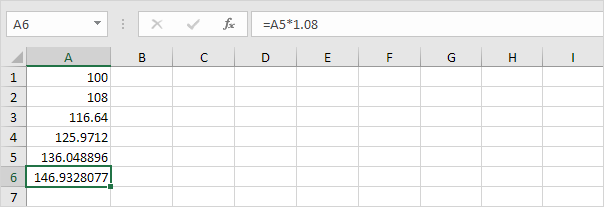
The answer is $146.93.
4. All we did was multiplying 100 by 1.08, 5 times. So we can also directly calculate the value of the investment after 5 years.
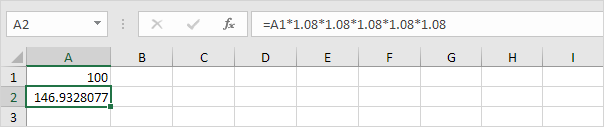
which is the same as:
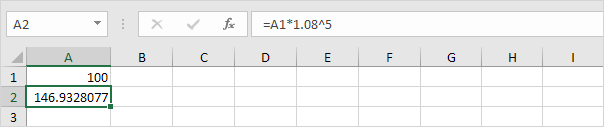
Note: there is no special function for compound interest in Excel. However, you can easily create a compound interest calculator to compare different rates and different durations.
5. Assume you put $10,000 into a bank. How much will your investment be worth after 10 years at an annual interest rate of 5% compounded monthly? The answer is $16,470.
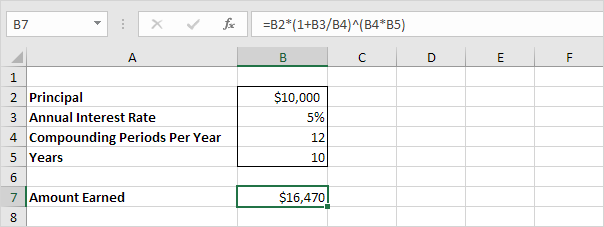
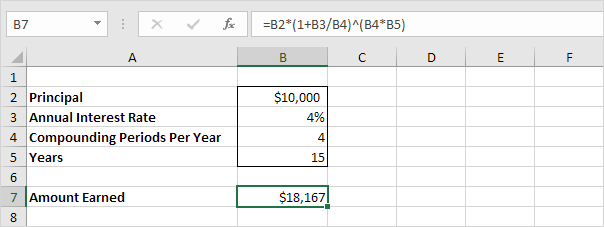
6. Assume you put $10,000 into a bank. How much will your investment be worth after 15 years at an annual interest rate of 4% compounded quarterly? The answer is $18,167.