How to get page from URL in Excel
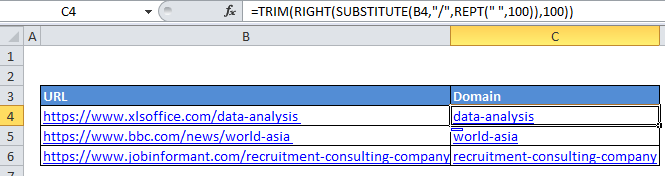
To extract the page, or the part of a path after the last forward slash (/), you can use a formula based on several Excel functions: TRIM, RIGHT, SUBSTITUTE, and REPT.
Formula
=TRIM(RIGHT(SUBSTITUTE(url,"/",REPT(" ",100)),100))
Explanation
In the example shown, the formula in C5 is:
=TRIM(RIGHT(SUBSTITUTE(B5,"/",REPT(" ",100)),100))
How this formula works
At the core, this formula replaces all forward slashes (/) with 100 spaces, then extracts 100 characters from the RIGHT and cleans this up with the TRIM function.
The replacement is done with SUBSTITUTE and REPT here:
SUBSTITUTE(B5,"/",REPT(" ",100))
Then, the RIGHT function extracts the last 100 characters of the string returned by SUBSTITUTE.
Finally, TRIM removes all leading and trailing space characters and returns the result.
Note: the use of 100 in this formula is arbitrary, and represents the maximum number of characters to be found after the final forward slash (/) in the original text. Adjust to suit your use case.