If cell is blank in Excel
This tutorial shows how to calculate If cell is blank in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=IF(A1="","blank","not blank")
Explanation
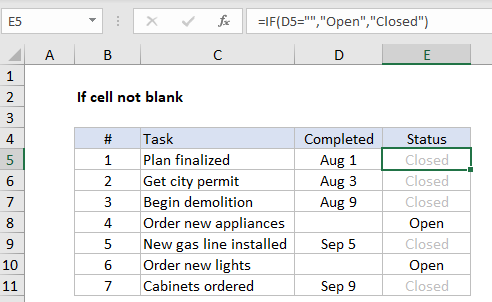
To test a cell and take some action if the cell is blank (empty), you can use the IF function. The formula in cell E5 is:
=IF(D5="","Open","Closed")
How this formula works
The logical expression =”” means “is empty”. In the example shown, column D contains a date if a task has been completed. In column E, a formula checks for blank cells in column D. If a cell is blank, the result is a status of “Open”. If the cell contains value (a date in this case, but it could be any value) the formula returns “Closed”.
The effect of showing “Closed” in light gray is accomplished with a conditional formatting rule.
Display nothing if cell is blank
To display nothing if a cell is blank, you can replace the “value if false” argument in the IF function with an empty string (“”) like this:
=IF(D5="","","Closed")
Alternative with ISBLANK
Excel contains a function made to test for blank cells called ISBLANK. To use the ISBLANK, you can revise the formula as follows:
=IF(ISBLANK(D5),"Open","Closed")