Force negative numbers to zero in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Force negative numbers to zero in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=MAX(value,0)
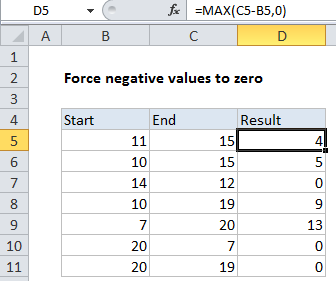
Explanation
To force negative numbers to zero without affecting positive numbers, you can use a formula based on the MAX function. In the example shown, the formula in D5 is:
=MAX(C5-B5,0)
How this formula works
This formula takes advantage of the fact that the MAX function works fine with small sets of data — even two values.
Inside MAX, the value in B5 is subtracted from the value in C5. If the result is positive, MAX will return the result as-is, since positive numbers are always greater than zero.
If the result if negative, MAX will return zero.
Replacement for IF
This formula is a clever way to avoid a more complicated IF formula. You can use the MIN and MAX functions to replace IF when you want to return the smaller or greater of two values.