Two-way lookup with INDEX and MATCH in Excel
This tutorial shows how to calculate Two-way lookup with INDEX and MATCH in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=INDEX(data,MATCH(val,rows,1),MATCH(val,columns,1))
Explanation
To lookup in value in a table using both rows and columns, you can build a formula that does a two-way lookup with INDEX and MATCH.
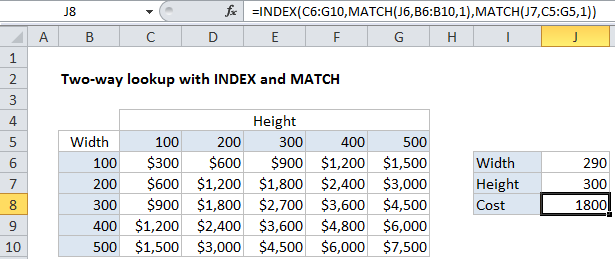
In the example shown, the formula in J8 is:
=INDEX(C6:G10,MATCH(J6,B6:B10,1),MATCH(J7,C5:G5,1))
Note that this formula is doing and “approximate match”, so row values and column values must be sorted.
How this formula works
The core of this formula is INDEX, which is simply retrieving a value from C6:G10 (the “data”) based on a row number and a column number.
=INDEX(C6:G10, row, column)
To get the row and column numbers, we use MATCH, configured for approximate match, by setting the 3rd argument to 1 (TRUE):
MATCH(J6,B6:B10,1) // get row number MATCH(J7,C5:G5,1) // get column number
In the example, MATCH will return 2 when width is 290, and 3 when height is 300.
In the end, the formula reduces to:
=INDEX(C6:G10, 2, 3) = 1800