Sum if not blank in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Sum if not blank in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUMIF(range,"<>",sum_range)
Explanation
To sum cells when certain values are not blank, you can use the SUMIF function.
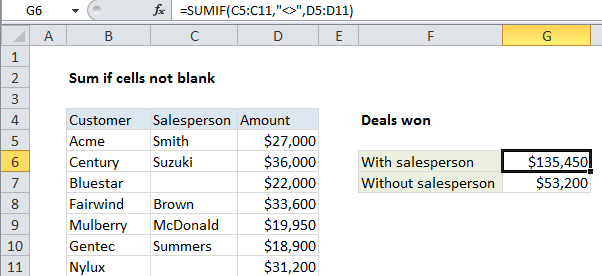
In the example shown, cell G6 contains this formula:
=SUMIF(C5:C11,"<>",D5:D11)
This formula sums the amounts in column D only when the value in column C is not blank
How the formula works
The SUMIF function supports all of the standard Excel operators, including not-equal-to, which is input as <>.
When you use an operator in the criteria for a function like SUMIF, you need to enclose it in double quotes (“”). When you use only “<>” in a criteria, you can think of the meaning as “not equal to empty”, or “not empty”.
Alternative with SUMIFS
You can also use the SUMIFS function sum if cells are not blank. SUMIFS can handle multiple criteria, and the order of the arguments is different from SUMIF. This SUMIFs formula is equivalent to the SUMIF formula above:
=SUMIFS(D5:D11, C5:C11,"<>")
With SUMIFs, the sum range always comes first.