Sum if by year in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Sum if by year in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUMIFS(sum_range,date,">="&DATE(year),date,"<="&DATE(year,12,31))
Explanation
If you need to sum if by year, you can use the SUMIFS function with two criteria.
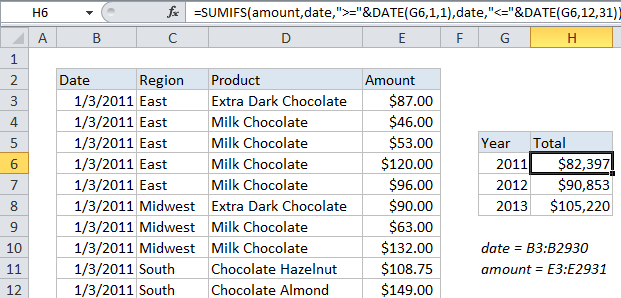
In the example shown, the formula in H6 is:
=SUMIFS(amount,date,">="&DATE(G6,1,1),date,"<="&DATE(G6,12,31))
The result is a total of amounts for 2011. When copied down, the formula also creates a total for 2012 and 2013.
How this formula works
The first argument for SUMIFs is always the range to sum (“sum_range”), and criteria are supplied as one or more range / criteria pairs.
In this example, the sum range is a named range called “amount” (E3:E2931), and the criteria are supplied in two pairs, both using a named range called “date” (B3:B2931).
In each case, the DATE function is used in the criteria to build two valid dates, both using with the same year:
1. The first day of 2011
2. The last day of 2011
These dates appear in the formula as follows:
date, ">="&DATE(G6,1,1) // date is >= to 1/1/2011 date, "<="&DATE(G6,12,31) // date is <= 12/31/2011
As a result, the formula returns a total sum for all amounts in the year 2011 only.
Because we are using a cell reference to supply the year, the formula can be copied down to create totals for 2012 and 2013 as well.