COUNTIFS with multiple criteria and OR logic in Excel
This tutorial shows how to COUNTIFS with multiple criteria and OR logic in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUM(COUNTIFS(range,{"red","blue","green"}))
Explanation
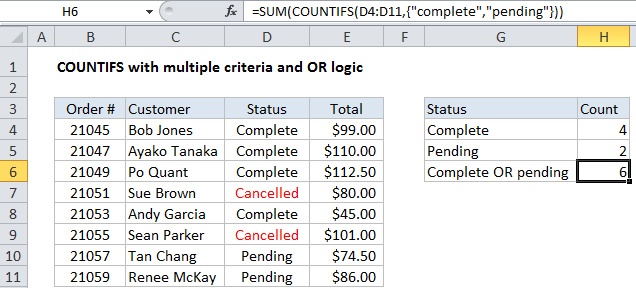
To count with multiple criteria and OR logic, you can use the COUNTIFS function with an array constant. In the example shown, the formula in H6 is:
=SUM(COUNTIFS(D4:D11,{"complete","pending"}))
How this formula works
By default, the COUNTIFS function applies AND logic. When you supply multiple conditions, all conditions must match in order to generate a count.
One solution is to supply multiple criteria in an array constant like this:
{"complete","pending"}
This will cause COUNTIFS to return two results: a count for “complete” and a count for “pending”, packaged in an array result like this:
{4,2}
To get a final total, we wrap COUNTIFS inside SUM. The SUM function then sums all items in the array and returns the result.
Adding another OR criteria
You can add one additional criteria to this formula, but you’ll need to use a single column arrayfor one criteria and a single row array for the other. So, for example, to count orders that are “Complete” or “Pending”, for either “Andy Garcia” or “Bob Jones”, you can use:
=SUM(COUNTIFS(D4:D11,{"complete","pending"},C4:C11,{"Bob Jones";"Andy Garcia"}))
Note we use a semi-colon for the second array constant, which creates a vertical array. This works because Excel “pairs” elements in the two array constants, and returns a two dimensional array of results inside SUM like this:
=SUM({1,0;1,0})
If you have more than two criteria, consider a SUMPRODUCT formula as described here.
Cell reference for criteria
To use a cell reference for criteria, you can use an array formula like this:
={SUM(COUNTIFS(range1,range2))}
Where range1 is the criteria range, and range2 contains criteria.
Wildcards and double-counting
COUNTIF and COUNTIFS support wildcards, but you need to be careful not to double count when you have multiple “contains” conditions with OR logic. See this example for more information