Count occurrences in entire Excel Workbook
This tutorial shows how to Count occurrences in entire Excel Workbook using the example below;
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT(COUNTIF(INDIRECT("'"&sheets&"'!"&range),criteria))
Explanation
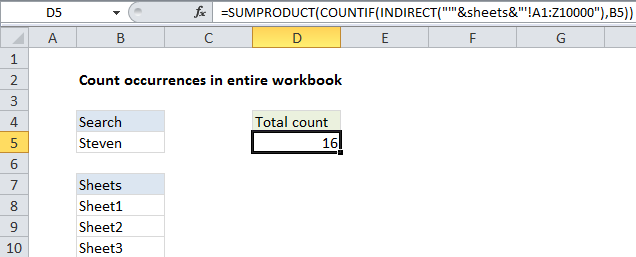
To count matches in entire workbook, you can use a formula based on the COUNTIF and SUMPRODUCT functions. In the example shown, the formula in D5 is:
=SUMPRODUCT(COUNTIF(INDIRECT("'"&sheets&"'!A1:Z10000"),B5))
where “sheets” is the named range B8:B10.
Context
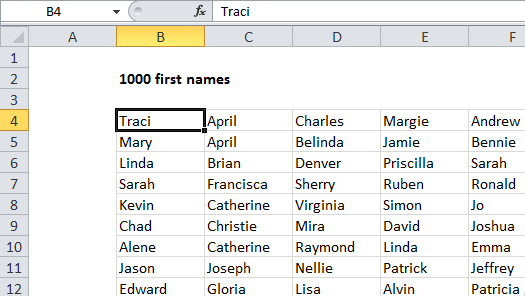
This workbook has four worksheets. Three of the worksheets, “Sheet1”, “Sheet2”, and “Sheet3” contain 1000 random first names in a table that looks like this:
Note: the range we are using in the formula, A1:Z10000, is arbitrary and should be adjusted to suit your data.
How this formula works
Working from the inside out, we first have this expression inside the INDIRECT function:
"'"&sheets&"'!A1:Z10000"
Because “sheets” is a named range that contains “Sheet1”, “Sheet2”, and “Sheet3”, we get an array like this once the expression is evaluated:
{"'Sheet1'!A1:Z10000";"'Sheet2'!A1:Z10000";"'Sheet3'!A1:Z10000"}
Inside the array, we have three values, and each is a sheet name joined via concatenation to the range A1:Z10000. Notice that these are all text values.
Next, the INDIRECT function is used to convert each text value to a proper reference, which are supplied to the COUNTIF function as the range argument, along with the value in D5 for criteria.
Since we’ve given COUNTIF three separate ranges, we get back three results in array like this:
{5;6;5}
Each item is a a count for one sheet.
Finally, SUMPRODUCT is used to sum the array, and returns a result of 16.