Count numbers that begin with in Excel
This tutorial shows how to Count numbers that begin with in Excel using the example below;
Formula
=SUMPRODUCT(--(LEFT(range,chars)="xx"))
Explanation
To count numbers in a range that begin with specific numbers, you can use a formula based on the SUMPRODUCT function and LEFT functions.
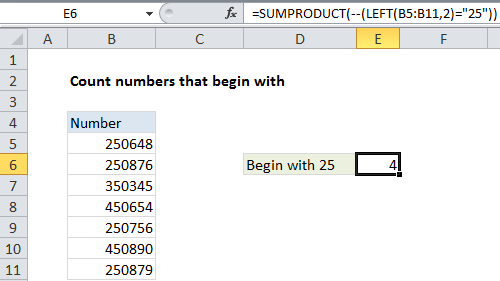
In the example shown, the formula in E6 is:
=SUMPRODUCT(--(LEFT(B5:B11,2)="25"))
How this formula works
Inside SUMPRODUCT, we use the LEFT function on the range of numbers like this:
LEFT(B5:B11,2)
This creates an array of results like this:
{"25";"25";"35";"45";"25";"45";"25"}
We then compare each value to “25” to force a TRUE or FALSE result. Note that LEFT automatically converts the numbers to text, so we use the text value “25” for the comparison. The result is an array of TRUE and FALSE values:
=SUMPRODUCT(--({TRUE;TRUE;FALSE;FALSE;TRUE;FALSE;TRUE}))
Next, we use a double negative co coerce TRUE FALSE values to 1 and zero, which creates a numeric array:
=SUMPRODUCT({1;1;0;0;1;0;1})
The SUMPRODUCT function then simply sums the elements in the array and returns 4.