How to use Excel ROW Function
This Excel tutorial explains how to use the ROW function with syntax and examples.
Excel ROW Function Description
Microsoft Excel ROW function returns the row number of a cell reference.
The ROW function is a built-in function in Excel that is categorized as a Lookup/Reference Function. The ROW function can be entered as part of a formula in a cell of a worksheet.
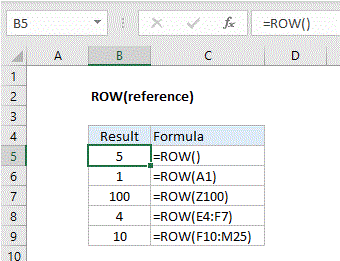
Explanation: The Excel ROW function returns the row number for a reference. For example, ROW(C5) returns 5, since C5 is the fifth row in the spreadsheet. When no reference is provided, ROW returns the row number of the cell which contains the formula.
ROW function is used to get the row number for a cell reference or a range. For example:
=ROW(A3) // returns 3 =ROW(D5) // returns 5 =ROW(F10:J15) // returns 10
Syntax
The syntax for the ROW function in Microsoft Excel is:
ROW( [reference] )
Arguments
- reference
- Optional. It is a reference to a cell or range of cells.
Returns
The ROW function returns a numeric value.